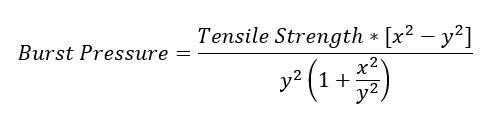How to determine the pressure rating of tubing?
To ensure that your desired tubing is fit for your needs, one must understand how pressure ratings affect different materials. If the material is chosen for inappropriate use, it can burst at the most inconvenient time; however, this can be prevented by using Barlow’s formula, which shows the theoretical maximum operating pressure of a tube by using its tensile strength at yield (maximum pressure at which there is no permanent damage) and its interior and exterior diameters. This formula can be used for all of your tubing needs, as it is based on a 4:1 safety factor, which is appropriate for compressed air and gases, as well as fluids with working pressure greater than 1MPa.
Barlow’s Formula
Burst Pressure in MPa or psi
Tensile Strength @ Yield in MPa or psi
X= OD/2 in inches
Y= ID/2 in inches
Tensile Strength Values
Click on a product to be redirected to its page.
| Material | Product | Tensile Strength @ Yield (psi) | Tensile Strength @ Yield (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phathalate Free Vynil | ClearGreen® | 1900 | 13.1 |
| ClearGreen®60 | 1700 | 11.7 | |
| Silicone (Non-Braided) | Platinum Cured Silicone | 1200 | 8.3 |
| Peroxide Cured Silicone | 1595 | 11 | |
| TPE | Pharm-A-Line™ I | 972 (At Break) | 6.7 |
| Pharm-A-Line™ VI | 2100 | 14.5 | |
| Weldable TPE | CellGyn® | 870 | 6 |
| PFA | Fluor-A-Pure™ PFA | 4200 | 28.9 |
| FEP | Fluor-A-Pure™ FEP | 4000 | 27.5 |
| PTFE | Fluor-A-Pure™ PTFE | 3500 | 24.1 |
| PVDF | Kynar-Flex® | 2000-3100 | 14-21 |
| LDPE | LDPE | 1700 | 11.7 |
| LLDPE | LLDPE | 2170 | 15 |
Note: These are theoretical values. Material properties may be affected greatly by temperature, operating pressure, chemical concentration, the presence of other chemicals, and other factors. Ultimately, users should determine the compatibility of any product through field testing under their particular process conditions.